How Many Colors Are In The Rainbow? Unlocking The Mysteries Of Nature's Palette
Have you ever found yourself gazing up at the sky after a rainstorm, marveling at the breathtaking arc of colors stretching across the horizon? How many colors are in the rainbow? It’s a question that has intrigued people for centuries, and today, we’re diving deep into this vibrant phenomenon to uncover the answers. Rainbows aren’t just pretty—they’re a scientific marvel that tells us so much about light, physics, and the wonders of nature. So, buckle up because we’re about to take a colorful ride through the science of rainbows!
But wait, why does this even matter? Understanding the colors in a rainbow isn’t just about satisfying our curiosity—it’s also about appreciating the beauty of the world around us. Whether you’re a science enthusiast, a teacher, or simply someone who loves staring at rainbows, knowing how many colors are in the rainbow can add a whole new layer of appreciation for this natural spectacle.
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty, let’s set the stage. Rainbows have been celebrated in art, mythology, and science for as long as humans have walked the Earth. They’ve inspired poets, fascinated scientists, and sparked countless debates. So, how many colors are there really? Let’s find out!
Read also:Peppa Pig House Wallpaper Transform Your Walls Into A Fun Adventure
Table of Contents
- Rainbow Basics: A Quick Overview
- The Seven Colors of the Rainbow
- How Rainbows Form: The Science Behind the Magic
- Variations in Rainbow Colors
- Cultural Significance of Rainbows
- Famous Rainbows Around the World
- Rainbow Myths and Legends
- Rainbow Science: Advanced Concepts
- Tips for Capturing Stunning Rainbow Photos
- Conclusion: Embrace the Rainbow
Rainbow Basics: A Quick Overview
Alright, let’s start with the basics. A rainbow is essentially an optical phenomenon caused by the interaction of sunlight with water droplets in the atmosphere. But here’s the kicker—it’s not just about the light bouncing around; it’s about the way our eyes perceive those bounces. When sunlight passes through raindrops, it bends, reflects, and spreads out into different wavelengths, creating the colorful display we all know and love.
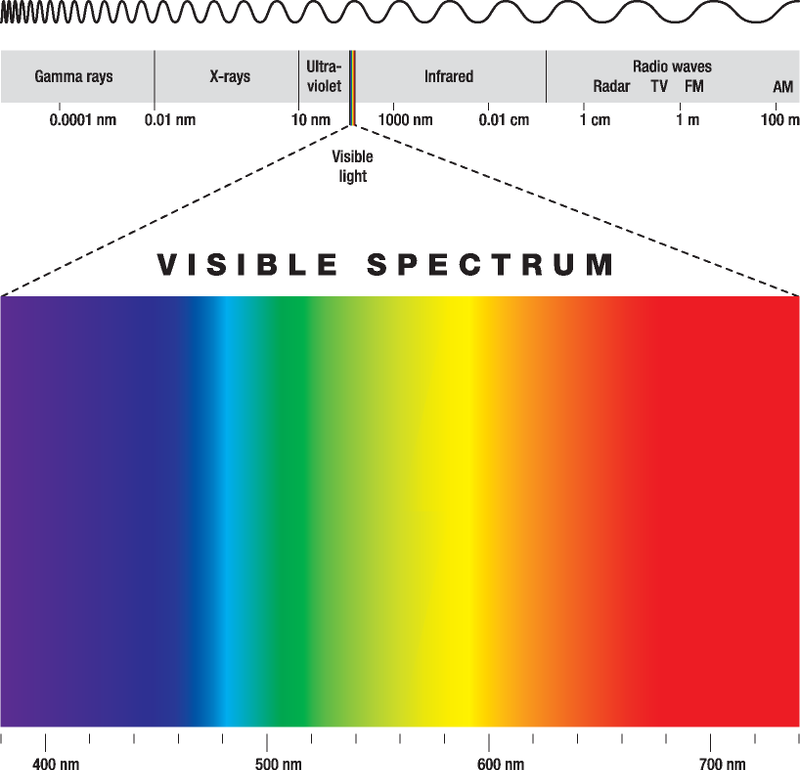
Now, when it comes to answering the question, "how many colors are in the rainbow," most people immediately think of the classic seven: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. But is that all there is to it? Well, not quite. Let’s break it down further.
The Seven Colors of the Rainbow
Let’s talk about the famous seven colors of the rainbow. These colors were first identified by Sir Isaac Newton, who used a prism to split white light into its individual components. Here they are:
- Red
- Orange
- Yellow
- Green
- Blue
- Indigo
- Violet
Newton named these colors based on the visible spectrum of light, and they’ve become the standard way we describe rainbows. But here’s a fun fact: the human eye can actually detect thousands of shades in between these colors, making the rainbow far more complex than it appears at first glance.
How Rainbows Form: The Science Behind the Magic
Ever wondered how rainbows actually form? It’s a fascinating process that involves light, water, and angles. When sunlight enters a raindrop, it slows down and bends, a process known as refraction. The light then reflects off the inside surface of the droplet and exits, bending again as it leaves. This bending causes the light to spread out into its constituent colors, creating the rainbow we see.
What’s even cooler is that the angle at which the light exits the raindrop determines the position of each color in the rainbow. For example, red light bends the least, while violet light bends the most. This is why red always appears on the outer edge of the rainbow, and violet is on the inner edge.
Read also:Sam Frankleaks The Inside Story You Need To Know About
Why Do We See Rainbows After Rain?
Simply put, rainbows appear after rain because the air is filled with tiny water droplets. These droplets act like prisms, splitting the sunlight into its component colors. But here’s the thing—you don’t need rain for a rainbow to form. Mist, fog, and even spray from waterfalls can create rainbows under the right conditions.
Variations in Rainbow Colors
Not all rainbows are created equal. While the classic seven colors are the most commonly observed, there are variations that can occur depending on atmospheric conditions. For example:
- Double Rainbows: These occur when light reflects twice inside a raindrop, creating a second, fainter arc above the primary one.
- Supernumerary Rainbows: These are faint, additional bands of color that appear inside the primary rainbow due to interference patterns.
- Moonbows: Also known as lunar rainbows, these occur when moonlight is refracted through raindrops, though they’re much fainter than daytime rainbows.
So, how many colors are in these variations? The answer depends on the specific conditions, but the principles remain the same.
Cultural Significance of Rainbows
Rainbows have played a significant role in cultures around the world. In many mythologies, they’re seen as bridges between the earthly and divine realms. For example:
- In Norse mythology, the rainbow is Bifrost, a bridge connecting Asgard to Midgard.
- In Greek mythology, Iris is the goddess of the rainbow, serving as a messenger between gods and mortals.
- In modern times, the rainbow has become a symbol of diversity, hope, and LGBTQ+ pride.
These cultural associations remind us that rainbows are more than just a natural phenomenon—they’re a source of inspiration and meaning for humanity.
Famous Rainbows Around the World
Some places are famous for their stunning rainbows. For instance:
- Hawaii: Known for its frequent and vibrant rainbows, Hawaii is often referred to as the "Rainbow Capital of the World."
- Ireland: The legend of the leprechaun’s pot of gold at the end of the rainbow has made Ireland synonymous with this natural wonder.
- Victoria Falls: Located on the border of Zambia and Zimbabwe, this waterfall is famous for its massive rainbows, which can sometimes be seen year-round.
These locations remind us that rainbows are not only beautiful but also tied to specific geographical and cultural contexts.
Rainbow Myths and Legends
From ancient times to the present day, rainbows have inspired countless myths and legends. Here are a few:
- In Aboriginal Australian culture, the rainbow serpent is a powerful creator deity associated with water and fertility.
- In Hindu mythology, Indra uses the rainbow as a bow to shoot lightning bolts.
- In Norse legend, the rainbow bridge Bifrost is guarded by the god Heimdall, who sounds his horn to warn of impending danger.
These stories highlight the universal fascination with rainbows across different cultures and eras.
Rainbow Science: Advanced Concepts
For those who want to dive deeper, there’s a lot more to rainbow science than meets the eye. Concepts like diffraction, polarization, and spectral distribution all play a role in how we perceive rainbows. For example:
- Diffraction: The bending of light waves around obstacles, which can create additional color patterns in rainbows.
- Polarization: The orientation of light waves, which affects how we see certain colors in a rainbow.
- Spectral Distribution: The range of wavelengths present in sunlight, which determines the colors we see.
These advanced concepts show that rainbows are not just pretty—they’re a window into the complexities of light and optics.
Tips for Capturing Stunning Rainbow Photos
If you’re a photography enthusiast, capturing a rainbow can be a rewarding challenge. Here are some tips:
- Use a wide-angle lens to capture the full arc of the rainbow.
- Set your camera to manual mode for better control over exposure and focus.
- Include foreground elements like trees or mountains to add depth to your shot.
- Experiment with different angles and perspectives to create unique compositions.
With these tips, you’ll be well on your way to capturing the perfect rainbow photo.
Conclusion: Embrace the Rainbow
So, how many colors are in the rainbow? While the classic answer is seven, the truth is far more complex and beautiful. Rainbows are not just a scientific phenomenon—they’re a source of inspiration, wonder, and cultural significance. Whether you’re marveling at a double rainbow in Hawaii or learning about the physics of light, rainbows remind us of the beauty and complexity of the world around us.
I invite you to leave a comment below sharing your favorite rainbow memory or experience. And if you enjoyed this article, don’t forget to share it with your friends and family. Together, let’s spread the joy of rainbows far and wide!