Countries With Birthright Citizenship: Your Ultimate Guide
When it comes to citizenship, there's nothing quite like being granted that status simply because you were born in a particular country. Birthright citizenship, also known as "jus soli," is a concept that has fascinated people worldwide. Imagine stepping into the world and instantly becoming a citizen of a nation, no paperwork or lengthy processes required. Sounds pretty sweet, right? But not all countries offer this privilege, and that's where things get interesting. In this article, we'll dive deep into the world of birthright citizenship and uncover which nations embrace this principle.
Birthright citizenship is more than just a legal term; it's a reflection of a country's values, history, and commitment to inclusivity. Some nations have embraced this idea for centuries, while others have debated and even abandoned it. So, why does birthright citizenship matter? Well, it plays a significant role in shaping global migration patterns, family dynamics, and even economic opportunities. Understanding which countries offer this benefit can be crucial for anyone planning to start a family or considering relocation.
Whether you're a curious traveler, an aspiring immigrant, or simply someone fascinated by global policies, this article is for you. We'll break down the concept of birthright citizenship, explore the countries that practice it, and delve into the pros and cons of this system. By the end of this read, you'll have a clearer picture of how this policy works and its implications on a global scale. Let's get started!
Read also:Nashville Man Brain Exposed A Shocking Medical Mystery Unveiled
Table of Contents
- What is Birthright Citizenship?
- Countries Offering Jus Soli
- The History of Birthright Citizenship
- Advantages of Jus Soli
- Disadvantages of Jus Soli
- Countries Abolishing Birthright Citizenship
- Legal Implications
- Birthright Citizenship in the US
- Comparison with Jus Sanguinis
- The Future of Birthright Citizenship
What is Birthright Citizenship?
Alright, let's break it down. Birthright citizenship, or "jus soli" in fancy Latin terms, means that if you're born in a specific country, you automatically become a citizen of that country, no questions asked. It's like getting a free membership to the nation's club just by showing up in the right place. Simple, right? But don't get too excited yet, because not every country plays by these rules.
This concept is rooted in the idea that where you're born should determine your nationality, rather than your parents' citizenship. It's a principle that has sparked debates worldwide, with some praising it for its inclusivity and others criticizing it for potential drawbacks. Think about it – if you were born in a country with birthright citizenship, you'd have access to all the rights, benefits, and responsibilities that come with being a citizen, even if your parents aren't from there.
Now, this doesn't mean every country is on board with this idea. In fact, only a handful of nations offer birthright citizenship. We'll dive deeper into that later, but first, let's explore why this concept even exists in the first place. Stick around, because it's about to get interesting!
Why Jus Soli Matters
Here's the deal: birthright citizenship isn't just about handing out passports willy-nilly. It's a powerful statement about a nation's values and priorities. Countries that embrace jus soli often do so because they believe in equality, diversity, and the idea that everyone deserves a fair shot. It's like saying, "Hey, no matter where you come from or who your parents are, you're part of our community now."
But there's more to it than just warm fuzzy feelings. Birthright citizenship can have a huge impact on immigration policies, economic growth, and even social cohesion. For instance, granting citizenship to children born on your soil can help reduce statelessness and ensure that everyone has access to basic rights and opportunities. On the flip side, some argue that it can encourage so-called "birth tourism," where people travel to specific countries just to give birth and secure citizenship for their kids. It's a complex issue, and we'll tackle the pros and cons later on.
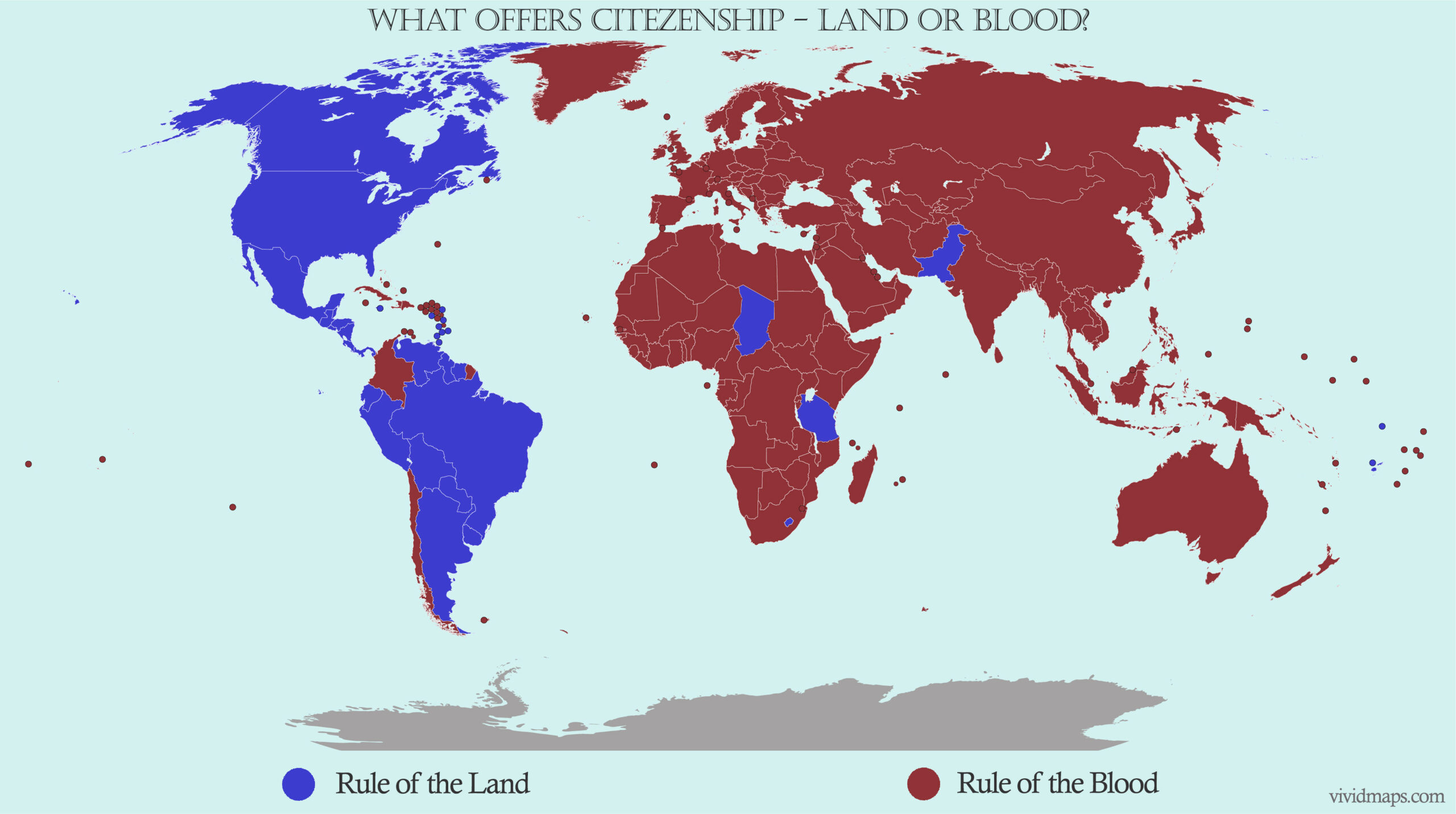
Countries Offering Jus Soli
So, which countries actually practice birthright citizenship? Well, buckle up, because the list is shorter than you might think. Out of the 195 countries in the world, only about 30 offer full birthright citizenship. That's right – just 30. And most of them are in the Americas, which is kind of interesting when you think about it.
Read also:Peppa Pig House Wallpaper Transform Your Walls Into A Fun Adventure
Some of the big names on this list include the United States, Canada, Brazil, Argentina, and Mexico. But there are also some surprising additions, like Guyana, Paraguay, and Uruguay. These countries have embraced jus soli for various reasons, whether it's to promote inclusivity, boost population growth, or strengthen national identity. It's like they're saying, "Hey, come one, come all – we want you here!"
Of course, not every country in the Americas offers birthright citizenship. Some, like Chile and Peru, have opted for a more restrictive approach, relying on "jus sanguinis" instead. We'll talk more about that later, but for now, let's focus on the countries that do offer this benefit. Here's a quick rundown of some of the key players:
Key Countries with Birthright Citizenship
- United States: One of the most well-known countries to offer birthright citizenship, the US has enshrined this principle in its Constitution. If you're born on US soil, you're automatically a citizen, no matter who your parents are.
- Canada: Our neighbors to the north also practice jus soli, making it a popular destination for immigrants and travelers alike.
- Brazil: As one of the largest countries in South America, Brazil has long embraced birthright citizenship as part of its national identity.
- Mexico: Birthright citizenship is alive and well in Mexico, where being born on Mexican soil grants you automatic citizenship.
- Argentina: Known for its rich history and vibrant culture, Argentina is another country that offers jus soli to anyone born within its borders.
The History of Birthright Citizenship
Now, let's take a trip back in time to understand how birthright citizenship came to be. Believe it or not, this concept has been around for centuries, with roots tracing back to ancient Rome and medieval Europe. Back in the day, being born on a particular piece of land often determined your allegiance to that kingdom or empire. It was all about geography and territory.
Fast forward to the modern era, and you'll find that birthright citizenship gained popularity in the Americas during the colonial period. As European powers established colonies in the New World, they brought with them a mix of legal traditions, including both jus soli and jus sanguinis. Over time, many countries in the Americas adopted jus soli as a way to build inclusive societies and integrate diverse populations.
But it wasn't all smooth sailing. Birthright citizenship has faced its share of challenges and controversies over the years. Some countries have debated whether to keep or abandon this principle, while others have implemented restrictions to address perceived abuses. It's a fascinating journey that continues to shape global citizenship policies today.
How Jus Soli Evolved Over Time
Here's a fun fact: the United States wasn't always a fan of birthright citizenship. It wasn't until the 14th Amendment was passed in 1868 that this principle was officially enshrined in US law. The amendment was designed to grant citizenship to former slaves and their descendants, ensuring that they had the same rights as other Americans. Since then, birthright citizenship has become a cornerstone of American identity, although it's still a topic of debate in political circles.
Other countries, like Canada and Brazil, have followed suit, incorporating jus soli into their legal frameworks. But the journey hasn't been without bumps. For example, in recent years, some politicians in the US and elsewhere have called for an end to birthright citizenship, arguing that it encourages illegal immigration and undermines national sovereignty. It's a heated debate that shows no signs of slowing down anytime soon.
Advantages of Jus Soli
So, what's so great about birthright citizenship? Well, for starters, it promotes inclusivity and equality. By granting citizenship to anyone born on its soil, a country sends a powerful message that everyone is welcome, regardless of their background. It's like saying, "We don't care where you came from – we care about where you're going."
Another big advantage is that jus soli helps reduce statelessness. Imagine being born without a nationality, unable to access basic rights like education, healthcare, or employment. Birthright citizenship ensures that no one is left behind, providing a safety net for children born in difficult circumstances. Plus, it can strengthen social cohesion by fostering a sense of belonging among diverse populations.
From an economic perspective, birthright citizenship can also be a boon. By welcoming newcomers and their families, countries can benefit from increased labor force participation, innovation, and cultural exchange. It's a win-win situation for everyone involved. But, of course, there are some downsides to consider, which we'll explore in the next section.
Economic Benefits of Birthright Citizenship
Let's talk numbers for a second. Studies have shown that countries with birthright citizenship tend to have more dynamic and diverse economies. By attracting immigrants and their families, these nations can tap into a wealth of talent, skills, and ideas. For example, the US has long been a hub for innovation, with many successful entrepreneurs and business leaders hailing from immigrant backgrounds.
But it's not just about the economy. Birthright citizenship also has social benefits, such as reducing poverty and improving educational outcomes. When children are granted citizenship at birth, they have better access to resources and opportunities, which can lead to a more prosperous and equitable society. It's like planting seeds for a brighter future – and who doesn't want that?
Disadvantages of Jus Soli
Of course, nothing is perfect, and birthright citizenship is no exception. One of the biggest criticisms of jus soli is that it can encourage so-called "birth tourism," where people travel to specific countries just to give birth and secure citizenship for their children. This practice has sparked debates about fairness and resource allocation, with some arguing that it places undue strain on public services.
Another concern is that birthright citizenship can create tensions between native-born citizens and immigrants. Some people worry that granting citizenship to everyone born on their soil dilutes national identity and undermines social cohesion. It's a complex issue that requires careful consideration and open dialogue.
Then there's the question of sustainability. In an era of increasing global mobility, some countries are rethinking their approach to citizenship, wondering if jus soli is still the best way forward. It's a valid concern, and one that deserves attention as we navigate the challenges of the 21st century.
Addressing Criticism of Birthright Citizenship
Now, let's be real – no system is perfect, and birthright citizenship is no exception. But that doesn't mean it's not worth defending. Many proponents of jus soli argue that its benefits far outweigh its drawbacks, pointing to its role in promoting inclusivity, reducing statelessness, and fostering economic growth. It's all about striking the right balance and addressing legitimate concerns without throwing the baby out with the bathwater.
Some countries have implemented measures to address these concerns, such as requiring parents to demonstrate a genuine connection to the nation before granting citizenship to their children. Others have opted for a hybrid approach, combining elements of jus soli and jus sanguinis to create a more nuanced system. It's a work in progress, but one that holds promise for the future.
Countries Abolishing Birthright Citizenship
Not all countries have stuck with birthright citizenship. In recent years, some nations have decided to abolish or restrict jus soli, citing concerns about immigration, resource allocation, and national identity. For example, Ireland famously ended its practice of birthright citizenship in